
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

A more general statement of the rule of product
|
|
If an object a1 can be chosen in m1 ways,
an object a2 can be chosen in m2 ways,
----------------------------------------------------
an object ak can be chosen in mk ways,
and if the choice of an object a1 does not affect the number of choices of a2, a3,…ak, the choice of a2 does not affect the number of choices of a3, a4,….ak, and so on then the choice of the ordered set of objects (a1, a2,…ak) in that order can be accomplished in
m1 * m2 * m3 * ….. * mk ways.
Example:
Signs are made which consist of a geometrical figure (a circle, square, triangle, hexagon [‘heksэgэn] – шестиугольник), a Russian letter and a decimal digit. How many signs can be mede? Such as
 B6 K8
B6 K8 
At first step we can choose a geometric figure. This can be done in 4 ways since we have a total of 4 figures. Then we can choose one of 32 Russian letters and finally one of 10 digits.
This brings the total to 4 x 33 x 10 = 1 320 combinations.
Suptopic: Permutations without repetitions:
The general statement of the problem is as follows: There are n-digit objects M = {a1, a2,…an}. Usually these objects are considered to be just numbers.
How many k – arrangements (ordered k – subsets) can be made out of these elements?
Two arrangements are considered distinct if they differ even by a single element or have a different sequence of elements.
Example: M = {a, b, c}.
2 – arrangement of the set M:
(a, b), (b, a), (a, c), (c, a), (b, c), (c, b).
3-arrangements of the same set:
(a, b, c), (a, c, b), (b, a, c), (b, c, a), (c, a, b), (c, b, a).
Such arrangements are termed permutations without repetitions.
The product 1 * 2 * 3 * …..* n is denoted by n! (is read: n – factorial).
It is agreed to consider 0! = 1.
The number of k-permutations out of n distinct objects is denoted by Ank.
The first element of any k – permutation can be chosen in n ways, the second element – in n – 1 ways and so on. Factually its k-th element can be chosen in n – k + 1 ways.
Applying the rule of product the necessary number of times we obtain:
Ank = n * ((n – 1) * (n – 2) * …. * (n – k + 1) =  (1)
(1)
This is number of k – arrangements of n distinct elements.
When n = k then we obtain out of expression (1):
Ann = Pn =  =
=  =
=  = n! (2)
= n! (2)
Let us write down an important relation for the number of k – permutations out of n elements;
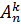 =
= 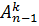 + k *
+ k *  ; (3)
; (3)
Relations of this type are called recursive (recurrence) relations.
We can prove that this equality is true in such a way:
If element 1 does not belong to a k – arrangement X, then X is a k-arrangement of the (n – 1)- set which is M – {1} (that is of the set M without the element 1).
Date: 2015-12-11; view: 491; Нарушение авторских прав