
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Sesamoid Bones
|
|
Sesamoid bones are usually short or irregular bones, imbedded in a tendon. The most obvious example of this is the Patella (knee cap) which sits within the Patella or Quadriceps tendon. Other sesamoid bones are the pisiform (smallest of the Carpals) and the two small bones at the base of the 1st Metatarsal. Sesamoid bones are usually present in a tendon where it passes over a joint which serves to protect the tendon. Types of Joints
A joint is the point where two or more bones meet. Tough bands of connective tissue called ligaments hold the bones of a joint in place. A tendon is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments and fascia as they are both made of collagen except that ligaments join one bone to another bone, and fascia connect muscles to other muscles. Tendons and muscles work together and can only exert a pulling force.
There are three main types of joints (see Figure 1): Fibrous (immoveable), Cartilaginous (partially moveable) and Synovia l (freely moveable).
Fibrous: This type of joint is held together by only a ligament. Examples are where the teeth are held to their bony sockets and at both the radioulnar and tibiofibular joints.
Cartilaginous: These joints occur where the connection between the articulating bones is made up of cartilage, for example between vertebrae in the spine.
Synovial: Synovial joints are by far the most common classification of joint within the human body. They are highly moveable and all have a synovial capsule (collagenous structure) surrounding the entire joint, a synovial membrane (the inner layer of the capsule) which secretes synovial fluid (a lubricating liquid) and cartilage known as hyaline cartilage which pads the ends of the articulating bones.
| Joint Examples | Type | Movement at joint |
| Hinge | Flexion / Extension | 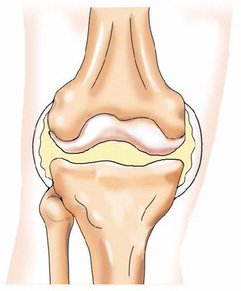 Elbow / Knee
Elbow / Knee
|
| Pivot | Rotation of one bone around another | 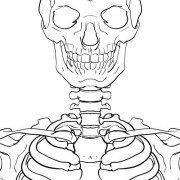 Top of the neck (atlas and axis bones)
Top of the neck (atlas and axis bones)
|
| Ball and Socket | Flexion / Extension / Adduction / Abduction / Internal and External Rotation | 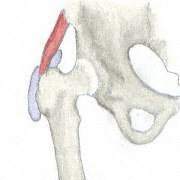 Shoulder / Hip
Shoulder / Hip
|
| Saddle | Flexion/Extension/Adduction/ Abduction/Circumduction | 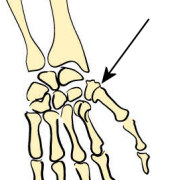 joint of the thumb
joint of the thumb
|
| Condyloid | Flexion / Extension / Adduction / Abduction / Circumduction | 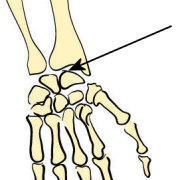 Wrist joints
Wrist joints
|
| Gliding | Gliding movements | 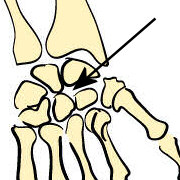 Intercarpal joints
Intercarpal joints
|
Figure 1. Types of joints
2. True or false statements. Make true with "T", false with "F". Correct the false statements.
1. _____Joint - tissue composed of fibres that can contract, causing movement of an organ or part of the body
2. _____Skeletal Muscle - the hard structure (bones and cartilages) that provides a frame for the body.
3. _____Ligament - a sheet or band of tough fibrous tissue connecting bones or cartilages or supporting muscles or organs.
4. _____Cartilage - a tough, elastic tissue that usually covers ends of bones.
5. _____The human body contains 246 bones.
6. _____The ribs curve and form a cage that protects the kidneys.
7. _____The internal portion of certain bones manufactures blood cells.
8. _____Diaphysis forms the larger rounded ends of long bones.
9. _____Osteoblasts are responsible for joint formation.
10. _____The periosteum provides a good blood supply to the bone.
11. _____There are 6 types of bone found within the human body.
12. _____Short bones are cranium and sternum.
3. Here are the answers to some questions from the text. What are the questions?
1. They function in the variety of ways.
2. They must also be light enough to make movement possible.
3. It consists of 4 sections.
4. Yes, it is. This is the long central shaft.
5. They are known as growth plates.
6. It happens between 18 and 25 years of age.
7. It can be divided into two layers.
8. They can be divided into 5 types.
9. This type of joint is held together by only a ligament.
10. It is the point where two or more bones meet.
11. Good examples of these are the vertebrae, sacrum and mandible.
12. They are as they sound, strong, flat plates of bone.
4. What do the following numbers refer to?
206, 25, 80, 20, 4, 5, 2.
Date: 2015-09-18; view: 869; Нарушение авторских прав