
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Read the text carefully to obtain detailed understanding of it. Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons
|
|
Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines the shape and symmetry of the body; acts as a protective device for your organs; acts as a firm base for the attachment of muscles (your muscles would not function properly without bones); and the marrow tissues in the cavity of the bones produces red cells and some white cells, required in your blood.
The human body contains 206 bones, which are organized into an internal framework called the skeleton. The bones, which make up the skeleton, function in the variety of ways. Bones and groups of bones support the muscles and organs, give shape and structure to the body and protect delicate internal organs. The ribs curve and form a cage that protects the heart and lungs. Similarly some skull bones, together called the cranium, form the protective case for the brain. Bones store calcium and phosphorus, important minerals used by the body in certain vital metabolism processes. In addition, the internal portion of certain bones manufactures blood cells.
Bone structure
It is important for bones to be strong enough to support our body weight, and, in some cases, provide protection such as the skull and ribs. However, they must also be light enough to make movement possible.
A long bone consists of several sections:
• Diaphysis: This is the long central shaft
• Epiphysis: Forms the larger rounded ends of long bones.
• Mctaphysis: The area between the diaphysis and epiphysis at both ends of the bone.
• Epiphyseal Plates: Plates of cartilage, also known as growth plates which allow the long bones to grow in length during childhood. Once we stop growing, between 18 and 25 years of age the cartilage plates stop producing cartilage cells and are gradually replaced by bone.
Covering the ends of bones, where they form a joint with another bone, there is a layer of hyaline cartilage. This is a firm but elastic type of cartilage which provides shock absorption to the joint and has no neural or vascular supply. If you were to cut a cross-section through a bone, you would first come across a thin layer of dense connective tissue known as periosteum. This can be divided into two layers, an outer "fibrous layer' containing mainly fibroblasts and an inner "cambium layer", containing progenitor cells which develop into osteoblasts (the cells responsible for bone formation). The periosteum provides a good blood supply to the bone and a point for muscular attachment.
Under the periosteum there is a thin layer of compact bone (often called cortical bone), which provides the bone's strength. It consists of tightly stacked layers of bone which appear to form a solid section, although do contain osteons, which like canals provide passageways through the hard bone matrix.
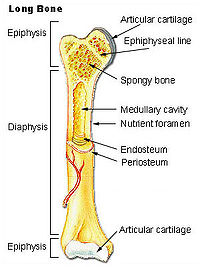 On the inside of this there is a different kind of bone, known as spongy bone. This is a more porous, lightweight type of bone with an irregular arrangement of tissue which allows maximum strength. In a long bone, this is normally found at either end of the bone, in flat or irregular bones it is a thin layer found just inside the compact bone. Interestingly, compact bone constitutes up to 80% of the bones weight, with spongy bone making up the additional 20%, despite its much larger surface area.
On the inside of this there is a different kind of bone, known as spongy bone. This is a more porous, lightweight type of bone with an irregular arrangement of tissue which allows maximum strength. In a long bone, this is normally found at either end of the bone, in flat or irregular bones it is a thin layer found just inside the compact bone. Interestingly, compact bone constitutes up to 80% of the bones weight, with spongy bone making up the additional 20%, despite its much larger surface area.
The centre of the bone shaft is hollow and known as the medullary cavity. This contains both red and yellow bone marrow. Yellow bone marrow is mainly a fatty tissue, while the red bone marrow is where the majority of blood cells are produced. This is found in higher proportions in the flat and irregular bones.
Date: 2015-09-18; view: 1376; Нарушение авторских прав