
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Nucleus role in transmission of hereditary information
|
|
Plan
1. Nucleic acids - carriers of genetic information
2. Chromosomes brief characteristic
3. Central dogma of molecular biology
4. Cytogenetics as the science of chromosomes
5. General plan of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
6. The unique structure of mitochondria
7. The main differences of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure
1. Nucleic acids - carriers of genetic information
It was known for a long time that chromosomes possess a unique molecular constituent, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), but there was not shown that this constituent carried genetic information. There weren’t direct evidences of gene chemical nature. In the early 1940s, research on the mold Neurospora by George W. Beadle and Edward Tatum supported the hypothesis of Archibald E. Garrod that genes work by controlling the synthesis of specific enzymes (the one gene-one enzyme hypothesis). Genetic information within genes determines the order of the 20 different amino acids within the polypeptide chains of proteins.
A complementary double helix was found in 1953 by Frances Crick and James Watson. In the double helix, the two DNA chains are held together by hydrogen bonds (a weak noncovalent chemical bond) between pairs of bases on the opposing strands. This base pairing is very specific: The purine adenine only base-pairs to the pyrimidine thymine, while the purine guanine only base-pairs to the pyrimidine cytosine. In double-helical DNA, the number of A residues must be equal to the number of T residues, while the number of G and C residues must also be equal (Chargaff's rules). As a result, the sequence of the bases of the two chains of a given double helix has a complementary relationship and the sequence of any DNA strand exactly defines that of its partner strand.
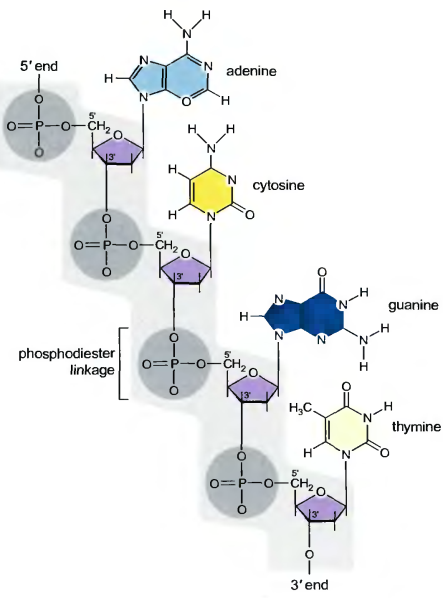
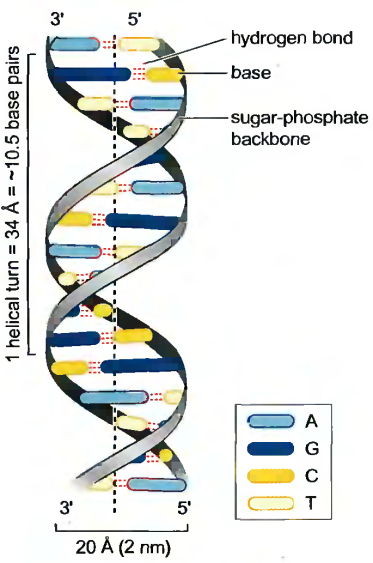
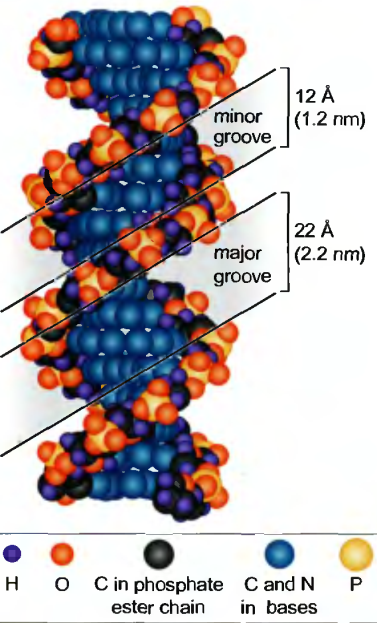
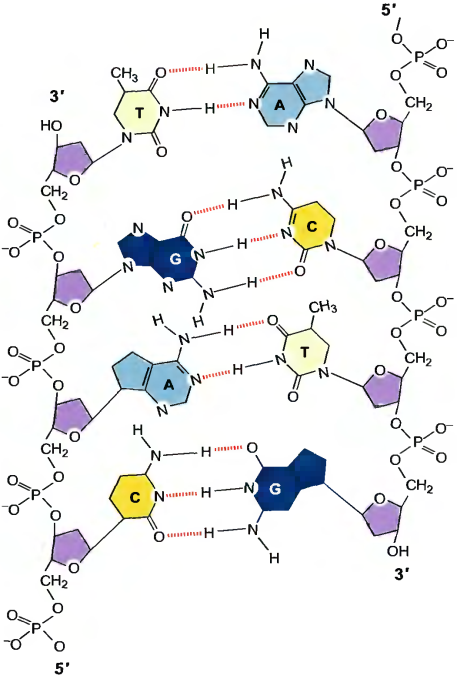
2. Chromosomes brief characteristic
Chromosome is a structural element of the cell nucleus, which is able to reproduce, and is composed of a large number of DNA and nuclear proteins of different types. The word ''chromosome'' comes from the Greek (''chroma'', color) and (''soma'', body) due to their property of being very strongly stained by particular dyes.
Date: 2015-09-02; view: 527; Нарушение авторских прав