
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Chi-Square Test
|
|
In order to evaluate a genetic hypothesis, we need a test that can convert deviations from expected values into the probability of such inequalities occurring by chance. This test must take into consideration the size of the sample and the number of variables (degrees of freedom). If the size of the sample is less than 16, segregation in the ratio 9:3:3:1 is impossible.
The chi-square test (pronounced ki-; symbolized x2) proposed by Karl Pearson (1857 – 1936) in 1901 includes all of these factors. It allows analyzing if the deviation of observed results from expected ones is random or consequential for any reason, statistically estimates the difference between empirical and theoretical expected results.
Using the chi-square it may be established whether actually received frequency of phenotypic classes corresponds to theoretically expect one. Chi-square is the sum of squared deviations from the theoretical of empirical frequencies, referred to the theoretical frequencies: 
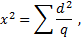
where d2  is squared deviations of each phenotype frequency from the theoretical value,
is squared deviations of each phenotype frequency from the theoretical value, 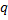 means theoretical frequencies of phenotypes appearance.
means theoretical frequencies of phenotypes appearance.
To find the value of chi-square it is necessary
· to calculate the difference between actual and calculated frequencies for each class,
· to make a square of differences and divide it to the calculated frequencies for each phenotypic class,
· to summarize the obtained relations.
If the chi-square is equal to 0, actually received frequency fully corresponds to the theoretical frequency. If the value is not 0, the table theoretical value of the standard chi-square test value for a given degrees of freedom and the chosen level of significance should be founded. If the experimental value is less than the standard, discrepancies between actual and theoretical expected frequencies are random and the null hypothesis (the assumption that between actually received and the calculated theoretical data is no significant difference) is retained; if more – rejected.
Thus, events probability that is neglected in the evaluation of the statistic parameter is expressed as accepted level of significance. Events probability when the hypothesis is true is called the confidence level.
Significance level 5% is assigned as P0.05, corresponding confidence level is P0.95. If P ≥ 0, 05 or P < 0, 95 the null hypothesis is retained, if P < 0, 05 or P ≥ 0, 95 – it is rejected.
Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Genetics - William D. Stansfield.pdf
Date: 2015-09-02; view: 438; Нарушение авторских прав