
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Задание 5. General view to determine the binding constants
|
|
Theory
General view to determine the binding constants
Comprehensive and interpretation of basic equations for host-guest complexation
The binding constant is used as a criterion for the evaluation of the host-guest complexation process. Thermodynamic parameters (enthalpy, entropy) and Gibbs free energy are more suitable criteria. In the case where Equations and hold good, thermodynamic parameters are related to each other as described in Figure 3 and Equation, the Vant’s Hoff equation. Theoretically, the determination of binding constants at different temperatures offers these thermodynamic parameters from the slope and intercept of the line in Figure 3. The important point in the quantitative analysis of host-guest complexation is how to determine the binding constant with high reliability.
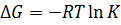

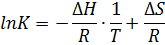
Our analysis to determine the binding constant is based on a simple binding equilibrium model. The binding constant, equilibrium constant, and stability constant are synonymous with each other. The activity coefficients are generally unknown and the stability constant K, based on the concentrations, is usually employed. Judging from this situation, the question of the activity coefficients if the solutes is disregarded here in order to simplify the discussion, Nevertheless, is should be remembered that this point is not always insignificant. The basic equations for host-guest complexation are the following four Equations.
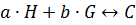
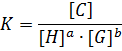
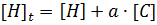
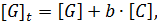
Where H is host; G, guest; C, complex; Ha ∙ Gb; a, b, stoichiometry: shown in Equation; [H]t, total concentration of host molecule at initial state; [G]t, total concentration of guest molecular at initial stage; [H], [G], [C], concentration of host, guest, and complex respectively at final stage, namely, at equilibrium.
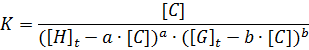
Parameters are classified into three as follows. Constants: K, a, b (a and b are integers larger than or equal to 1). Variables which can be set up as experimental condition: [H]t, [G]t. Variables dependent on each equilibrium: [H], [G], [C].
Experimental guideline from the theory
From Equation and the classification of its parameters is elucidated the guideline of the experiment. When [C] is obtained under equilibrium in which a and b are known, K is derived directly according to Equation from the experimental condition [H]t, and [G]t. Consequently, in order to determine the binding constants, the following four tasks have to be carried out.
· Determination of stoichiometry, namely, a and b
· Evaluation of [C]
· Setting up the concentration conditions [H]t and [G]t
· Data-treatment
The following sections deal with the principle and also the practical issues necessary for an understanding and completion of the above four tasks in this order.
Date: 2015-08-15; view: 329; Нарушение авторских прав