
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Приложение 2. Основные арифметические выражения, формулы, уравнения и правила их чтения на английском языке. ( ) round brackets; parentheses {
|
|
Основные арифметические выражения, формулы, уравнения
и правила их чтения на английском языке.
| () | round brackets; parentheses |
| { } | curly brackets; braces |
| [ ] | square brackets; brackets |
| a = b | a equals b; or a is equal to b |
| a ≠ b | a is not equal to b |
| a > b | a is greater than b |
| a2 > ad | a second is greater than a dth |
| b < a | b is less than a |
| a >> b | a is substantially greater than b |
| a ≥ b | a is greater than or equal to b |
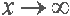
| x trends to infinity |
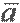
| a vector; the mean volume of a |
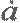
| the first derivative |
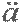
| the second derivative |
| 9.510 | nine thousand five hundred and ten |
| 32 + 8 = 40 | thirty-two plus eight is (are) forty; or, thirty-two plus eight equals forty; or, thirty-two plus eight is equal to forty; or, eight added to thirty-two makes forty |
| 20 - 5 = 15 | twenty minus five is fifteen; or, twenty minus five is equal to (equals) fifteen; or, twenty minus five leaves fifteen; or, five from twenty is (leaves) fifteen |
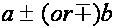
| a plus or minus b |
| 1 × 1 = 1 | once one is one |
| 2 × 2 = 4 | twice two is (equals) four; or, twice two makes four |
| 6 × 10 = 60 | six multiplied by ten equals sixty; or, six multiplied by ten is (equal to) sixty; or, six times ten is sixty |
| work = force × distance | work is (equal' to) the product of the force multiplied by the distance; or, work is (equal to) the product of force times the distance |
| 12: 3 = 4 | twelve divided by three equals (is) four |
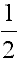
| a (one) half |
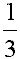
| a (one) third |
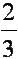
| two-thirds |
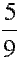
| five-ninths |
| 4½ | four and a half |
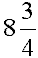
| eight and three-quarters |
| 0.6 or.6 | point six |
| 5.34 | five point thirty-four; or, five point three four |
| 2.01 | two point nought one; or two point o [ou] one |
| 0.007 | point nought nought seven; or, point two oes [ouz] seven |
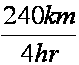
| 240 kilometers pro 4 hours |
| 8: 4 = 2 | the ratio of eight to four is two. |
20: 5 = 16: 4 or 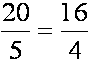
| the ratio of twenty to five equals (is equal to) the ratio of sixteen to four; or, twenty is to five as sixteen is to four |
| 20° | twenty degrees |
| 6´ | six minutes; also, six f eet |
| 10´´ | ten seconds; also, ten inches |
| a´ | a prime |
| a´´ | a second prime; or a double prime; or a twice dashed |
| a´´´ | a triple prime |
| 92 | nine square, or, the square of nine or, nine to the second power |
| 63 | six cubed; or, six to the third (power) |
| c18 | c [si:] to the eighteenth (power) |
| a-10 | a [ei] to the minus tenth (power) |
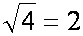
| the square root (out) of four is (equals) two |
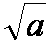
| the square root of a |
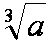
| the cube root of a |
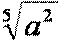
| the fifth root of a square |
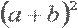
| a plus b all squared |
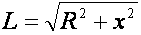
| L equals the square root (out) of R square plus x square |
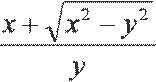
| x plus square root of x square minus y square all over y |
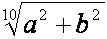
| the tenth root (out) of a square plus b square |
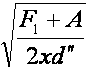
| square root out of F first plus A divided by two xd th twice dashed (or double prime) |
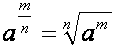
| a to the m/n th power equals the nth root out of a to the mth (power) |
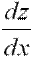
| dz over dx |
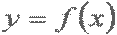
| y is a function of x |
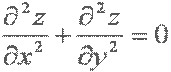
| partial d two z over partial dx plus partial d two z over partial dy equals zero |
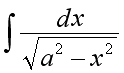
| indefinite integral of dx (divided) by the square root out of a2 minus x2 |
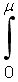
| integral from zero to µ (mu) |
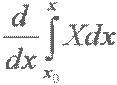
| d (divided) by dx (or d over dx) of the integral from x nought to x of X large dx |
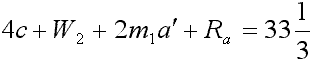
| 4c plus W second plus 2 m first a prime plus R ath equals thirty-three and one-third |
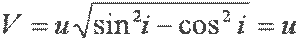
| V equals u square root of sine square i minus cosine square i equals u |
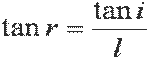
| tangent r equals tangent i divided by l |
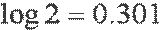
| the logarithm of two equals zero point three o[ou] one |
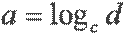
| a is equal to the logarithm of d to the base c |

| u is equal to the integral of f sub one of x multiplied by dx plus the integral of f sub two of y multiplied by dy |
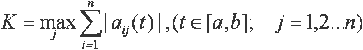
| K is equal to the maximum over j of the sum from i equals one to i equals n of the modulus of aij of t, where t lies in the closed interval ab and where j runs from one to n |
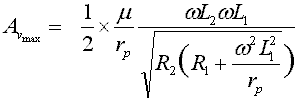
| A vmax is equal to one half mu by r pth omega L second omega L first (divided) by square root out of R second round brackets opened R first plus omega square L first square by r pth round brackets closed |

| Av is equal to mu omega m omega square L square (divided) by r pth square brackets opened omega square m square plus R second round brackets opened R first plus omega square L square (divided) by r pth round and square brackets closed |
| <== предыдущая | | | следующая ==> |
| Основы построения английского предложения | | | Основные классы неорганических соединений |
Date: 2015-09-18; view: 378; Нарушение авторских прав