
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Rules of working with the corpse
|
|
The dead person is undressed and laid on his back. Any valuable objects are taken off in the presence of attending doctor or doctor who’s on duty, which are then taken away for safekeeping. If the valuable object cannot be taken off it is written down into the patients history and his body is sent into the morgue with it.
The lower jaw is tied up, the eyelids are closed, the body is covered with bedsheet and left for 2 hours.
On the patient’s hip the full name and number of patient’s history is written.
The body is accompanied with the note that contains not only the full name and number of patient’s history, but also the diagnosis and date of death.
The corpse is transported with the nurse into morbid anatomy department.
Medical care provided for patients with respiratory diseases
Basic symptoms, characteristic for respiratory diseases, include cough, hemoptysis, pain in the chest, dyspnea, asphyxia.
One of the most frequent symptoms ofrespiratory diseases is a sharp expiration which results inclearing of bronchi from sputum and foreign bodies which have accumulated in it,it appears as a result of an inflammatory, mechanical, chemical or thermal irritation of coughing receptors located in larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles.
Tussis can lead to certain complications:
• Syncopal attacks (incidental loss of consciousness at the peak of tussis),
• Breaking of emphysematous bulla of a lung with development of pneumothorax and even fracture of ribs (in case of pathological changes to osteal tissue).
Hemoptysis is blood appearance in sputum. This state often precedes pulmonary bleeding. The hemoptysis causes: bronchitis, bronchoectatic disease, pulmonary tuberculosis, lung abscess, pneumonia, lung cancer, thromboembolism of pulmonary artery, mitral stenosis, lung edema, lung trauma, primary pulmonary hypertension, hemorrhagic diathesis. The blood excreted with tussis, is admixed with sputum, has scarlet colour and is foamy. The help patients in hemoptysis and development of pulmonary bleeding it is necessary:
1) to raise patient in bed.
2) for prevention of penetration of blood in other bronchi it is desirable to lie the patient on the damaged side.
3) in case of excitation it is necessary to prescribe sedative drugs,calm the patient, forbid him to talk.
4) forrelief (arrest) of tussis antitussives such as Codein, Codterpin, Codeinphosphate are prescribed.
5) apply ice bag to the chest, give small (0,5-1 cm in diameter) ice cubes to swallow.
6) bydoctor prescriptioncalcium gluconate is intravenously infused, Vicasol, γ-aminocaproic acid, blood, dry plasma, blood substitutes are transfused.
It is strictly forbidden in hemoptussisand pulmonary bleeding to applycupping glasses, mustard plasters, physiotherapy!
• Dyspnea is a change of frequency, depth, and rhythm of respiration, ratio distortion between inspiratory and expiratory phases, accompanied, as a rule, by subjective sensation of air shortage. In standard conditions frequency of respiratory movements in healthy people is from 14 to 20 per minute.
• • Shallow breathing can emerge in diseases of lungs, pleura lesion, severe abdominal pains, intensified duringdeep breathing or oppression of respiratory centre by morphine. It is manifested by depression of respiratory movementsamplitude of the chest.
• • Deepbreathingdevelopsin stimulation of respiratory centre by excess of lactic acid (metabolic acidosis), it is observed in diabetic coma, uremia, physical strain. It is characterised by the increase of respiratory movementsamplitude of thorax. It can be accompanied by tachypnea, bradipnoe,rhythm disorders.
• • The tachypnea is seen in case of body temperature increase, reduction of respiratory surface of the lungs, pulmonary edema, acidosis.
Methods of oxygen application (localand general application of oxygen):
• Local application of oxygen is indicatedin treatment of wounds contaminated with anaerobic infection, flaccid inflammatory processes, trophic disorders. In local use oxygen can be introduced subconjunctivally, retrobulbarly, into anterior chamber, intrapleurally, intraabdominally, into joint cavity, intraosteal, subcutaneously, cutaneously (general and local oxygen baths).
• Inhalation and non-inhalation method of application. It is carried out by means of masks, nasal catheters, intubation and tracheostomy tubes. In pediatric practice nowadayswe apply oxygen tents, inhalation by means of oxygen bag. Necessary condition of mask inhalation is humidifying and warming of oxygen. It prevents drying of mucosas of respiratory tracts and provides normal function of bronchi epithelium. Humidifying is done by passing oxygen through the pot with water (Bobrovapparatus). Humidity of gas in this case reaches 50 %.
Oxygen bag consists of rubber container for oxygen, rubber tube and mouthpiece. When filling the bagthe mouthpiece is taken out, rubber tube is put on the oxygen pressure regulator cock. After filling of the bag the pressure reducing valve is closed and the tube is pressed with a clamp. Mouthpiece is disinfected by wiping withcotton woolwet with alcohol. Oxygen humidifying is achievedby wrappingthe mouthpiece inside wet gauze napkins.
Hyperbaric oxygenation - medical application of oxygen under pressure more than 1 atmosphere. For this purpose we use single and multi-seater chambers. Indications to use: acute disturbances of passability of peripheral, coronary, cerebral vessels, blood loss, poisonings, shock, gas embolism, anaerobic infection, treatment ofnonhealing wounds, ulcers, surgical correction of congenital cardiacdisorders.
Enteral introduction of oxygen (oxygen cocktails) isan example of non-inhalation methods.
For diagnostic pleurocentesis the following is necessary:
• Alcohol, iodine for disinfection of the puncture site; sterile cotton wool balls and gauze napkins (10Х10 cm); sterile linen; cleolum, plaster; local anaesthesia set: 0,5 % solution of Novocaine, needles for intradermal and intramuscular injection, two 5-10 ml syringes, sterile syringe 20-50 ml; hypodermic puncture needles 10 cm long and in diameter 1mm; heparin solution (1000 Units/ml); sterile and unsterile basins for pleural fluid; 0,1 % solution of atropine and Cordiamin for hypodermic injections; two radiograms of thorax (frontal and lateral projections).
The choice of a puncture site in diagnostic pleurocentesis is done depending on the exudate location,not only physical data, but also including radiography and ultrasonic equipment.
• In all cases the needle is introduced on the upper edge of a rib, because on its lower edge there is a vascular-nervousbundleand if damagedit can cause serious complications.
The order of actions in pleurocentesis:
• Puncture area within the radius of 10 cm is smeared with 5% iodine tincture. Then iodine is then removed with sterile swabwet with alcohol. It is necessary for prevention of penetration of iodine into pleural cavity where it can cause formation of commissures.
• Puncture area is surrounded by sterile linen. First intradermal, then hypodermic introduction of 0,5% solution of Novocaine,periosteum anaesthesia, infiltration anaesthesia of intercostal muscles, pleura. The needle is introduced with pauses, after each 2 mm of insertion 0,2 ml of Novocaine is injected. When piercing parietal pleura there is a sensation of "fall-through". After that the piston of the syringe is pulled. Appearance in the syringe along with Novocaine of pleural fluid speaks about penetration of pleural cavity.
Remember! Pleural fluid may not appear in syringe in the following cases: the needle pierces the thin layer of pleural fluid, in absence of pleural fluid; the needle is introducedhigher (into lung) or lower (in abdominal cavity) than pleural exudate.
• After anaesthesia the needle is taken out of thorax and in this place puncture pleural cavity with a special needle with syringe of 20-50 ml that has 1 ml (1000 Units/ml) heparin solution for prevention of pleural fluidcoagulation. Take pleural fluid into the syringe. After removal of the needle on the place of puncture put gauze wad moistened with alcohol, atop of it put sterile gauze napkin, which is fixed to chest wall with plaster or cleolum.
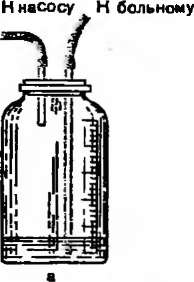

Pleurocentesis complications:
- -as a result of irritation of leaves of pleura vasovagal reflex can develop, it is characterised by appearance of rare weak filling of pulse, depression of arterial pressure
- - Pneumothorax
- - Infectioning of pleural cavity
- - As a result of intercostal artery damage hemothorax development is possible
-- Pulmonary edema after stretchingof the lung is connected withsignificant decrease of intrapleural pressure.
-- Rare complications are damages to liver, spleen, intestine, infectioning of soft tissues, spreading of tumour cells on the course of needle introduction.
Patient care in case of blood circulation diseases
The basic symptoms of blood circulation pathologiesare: pains in the area of heart or behind the breast bone, palpitation, faults in cardiac performance, dyspnea, edemata.
First aid for heartaches: sharply limit physical activity of the patient, lay or sit him, calm him down. On heart area and breast bone apply mustard plasters. Under the tongue the patient puts 1 pill of nitroglycerol. If pains in the heart area or behind breast bone were not stopped after these actions during 3-5 minutes, it is necessary to call the doctor.
Very characteristic sign of cardiac pathology is dyspnea that is intensified in horizontal and reduced in vertical position. It happens because in horizontal position venous blood inflows to the heart and pulmonary vessels easier, and the outflow from left ventricle is more difficult. Urgent aid:
— It is necessary to limit physical activity and calm the patient, place him in bed in semisitting position with lowered feet.
— On the extremitiesto reduce venous inflow to heart it is necessary to apply tourniquets. After correctapplication of tourniquet extremity becomes blue, veins bulk up, but the pulsing of peripheral arteries still can befelt. Such tourniquets on extremities are applied for 30 minutes
— To reducethe volume of circulating blood bloodletting in volume of 400 ml is done.
— Oxygenotherapyusing a mask with oxygen rate of 8-10 l/min or by means of catheter introduced into the nose with oxygen rate of 6 l/min.
Edemata in case of cardiacinsufficiency- result of stagnation of blood in greater circulation and fluid accumulation in organism. Cardiac edemata are localised more often on feet if the patient walks, or in the area of sacrum, loin, scapulas if the patient lies. The skin in the area of edema becomes smooth, shiny, tense, after pressing it long lasting fold is formed. In neglected cases of cardiac insufficiency the fluid (transudate) mayaccumulate in serous cavities.
— Асцит (греч. askites - похожий на раздутый мех, отёчный) - скопление жидкости в брюшной полости («водянка» живота).
— Ascites (Greek askites - similar to swollen fur, edematic) - fluid accumulation in abdominal cavity (abdominal "dropsy").
— Hydrothorax (Greek hydor - water, fluid, thorakos – thorax, chest) - fluid accumulation in pleural cavity.
— Hydropericardium(hydro + pericardium) - fluid accumulation in pericardium cavity.
— Anasarca (Greek ana - everywhere, sarcus - meat) - widespread edema of hypodermic tissue.
— Frequency. P ulse rate is the number of pulse waves per 1 minute. In norm pulse rate is 60-90 beats per 1 minute.Increase of frequency of cardiaccontractions for more than 90 per minuteis tachycardia. Reduction of number of cardiac contractions for less than 60 beatsper minute is bradycardia.
— Tension. It is defined by the force, which is applied during pressing on arterywalls to stop pulsing. By the degree of pulse strain it is possible to guess maximal pressure: the higher it is, the more tense pulse is.
— Filling. It is defined by quantity of blood that forms pulse wave, and depends on the systolic volume of heart. In good filling of pulse it is possible to feel with fingers high pulse wave, and in bad –weak pulse when pulse waves are small, poorly discernible. Hardly noticeablepulse is called threadlike.
— Rhythm. In norm pulse waves follow one after another at regular intervals. Heart rhythm disorder can manifest itself as extrasystole –out-of-turncontraction of heart under the influence of an impulse which has arisen outside sinus node. Extrasystolemanifests in the form of out-of-turn pulse wave of smaller filling (ventricles in diastole have not time to be filled with blood) after which the compensatory pause follows. Atrial extrasystoles can be in healthy people after abundant food intake, coffee, tea, smoking. Frequent ventricular extrasystoles are dangerous with their development into ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation of ventricles; in this connection after their appearance it is necessary to call the doctor immediately.
Special care is required by patients with chronic cardiac failure. One of the signs of circulatory insufficiency is edemas. In the process of progressing of cardiac failure edemas spread from feet and cruraonto hips, loin, abdomen, and chest. Long existing edemas result in disturbance of trophicity of tissues and formation of non-healing ulcers. After injections in the skin of such patients there are small holes left from which edematic fluid exudes. In this case it is necessary to smear the place of injection with iodine, and apply an aseptic bandage. The period of obvious edemas is preceded by the period of the latent fluid retention which can be detected by daily weighing the patient.
For determination of treatment efficiency it is necessary to monitor interrelation between the amount of urine (diuresis) excreted and liquid introduced into the organism.Diuresis estimation is done the following way. After urination at 6 a.m.during the day the patient urinates into the graduated container. Next morning the gathered data together with the body mass of the patient, amount ofliquid introduced into organism are written into patient’s history.
In cardiologic department there should be everything that might be necessary for reanimation activities and intensive care (cardiomonitors, electrocardiographs, electrical defibrillators, artificial lung ventilation equipment (including manual), laryngoscopes with endotracheal tubes, suction machines, sphygmomanometers for measuring arterial pressure, toolkit for tracheostomy, needles for intracardiac introduction of medication, sterile dressing material).
Among medical drugsthe department should have cardiac glycosides, periphericvasodilators, diuretics, antiarrhythmics, vasoconstrictors (adrenaline, noradrenaline), anticoagulants, narcotic analgetics.
Date: 2016-07-18; view: 432; Нарушение авторских прав