
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Confederacy surrenders
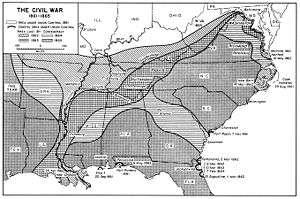
Map of Confederate territory losses year by year
Main article: Conclusion of the American Civil War
Initially, Lee was not intending to surrender, but rather to regroup at the village of Appomattox Court House, where supplies were to be waiting, and to continue the war. Grant chased Lee, and got in front of him, so that when Lee's army reached Appomattox Court House, they were surrounded. After an initial battle, Lee decided that the fight was now hopeless, and so he surrendered his Army of Northern Virginia on April 9, 1865, at the McLean House.[205] In an untraditional gesture and as a sign of Grant's respect and anticipation of peacefully restoring Confederate states to the Union, Lee was permitted to keep his sword and his horse, Traveller. On April 14, 1865, President Lincoln was shot by John Wilkes Booth, a Southern sympathizer. Lincoln died early the next morning, and Andrew Johnson became the president. Meanwhile, Confederate forces across the South surrendered as news of Lee's surrender reached them.[206] President Johnson officially declared a virtual end to the insurrection on May 9, 1865; Confederate President Jefferson Davis was captured the following day.[1] On June 23, 1865, Cherokee leader Stand Watie was the last Confederate General to surrender his forces.[207]
Diplomacy
Main articles: Britain in the American Civil War and France in the American Civil War
Europe in the 1860s was more fragmented than it had been since before the American Revolution. France was in a weakened state while Britain was still shocked by its own poor performance in the Crimean War.[208] France was unable or unwilling to support either side without Britain, where popular support remained with the Union though elite opinion was more varied. They were further distracted by Germany and Italy, who were experiencing unification troubles, and by Russia, who was almost unflinching in its support for the Union.[208][209]
Though the Confederacy hoped that Britain and France would join them against the Union, this was never likely, and so they instead tried to bring Britain and France in as mediators.[208][209] The Union, under Lincoln and Secretary of State William H. Seward worked to block this, and threatened war if any country officially recognized the existence of the Confederate States of America. In 1861, Southerners voluntarily embargoed cotton shipments, hoping to start an economic depression in Europe that would force Britain to enter the war to get cotton, but this did not work.[210] Worse, Europe developed other cotton suppliers, which they found superior, hindering the South's recovery after the war.

Crewmembers of USS Wissahickon by the ship's 11-inch (280 mm) Dahlgren gun, circa 1863
Cotton diplomacy proved a failure as Europe had a surplus of cotton, while the 1860–62 crop failures in Europe made the North's grain exports of critical importance. It also helped to turn European opinion further away from the Confederacy. It was said that "King Corn was more powerful than King Cotton", as U.S. grain went from a quarter of the British import trade to almost half.[210] When Britain did face a cotton shortage, it was temporary, being replaced by increased cultivation in Egypt and India. Meanwhile, the war created employment for arms makers, ironworkers, and British ships to transport weapons.[211]
Charles Francis Adams proved particularly adept as minister to Britain for the U.S. and Britain was reluctant to boldly challenge the blockade. The Confederacy purchased several warships from commercial ship builders in Britain (CSS Alabama, CSS Shenandoah, CSS Tennessee, CSS Tallahassee, CSS Florida and some others). The most famous, the CSS Alabama, did considerable damage and led to serious postwar disputes. However, public opinion against slavery created a political liability for European politicians, especially in Britain (which had abolished slavery in her colonies in 1834).[212]
War loomed in late 1861 between the U.S. and Britain over the Trent Affair, involving the U.S. Navy's boarding of a British mail steamer to seize two Confederate diplomats. However, London and Washington were able to smooth over the problem after Lincoln released the two. In 1862, the British considered mediation - though even such an offer would have risked war with the U.S. Lord Palmerston reportedly read Uncle Tom's Cabin three times when deciding on this.[212]
The Union victory in the Battle of Antietam caused them to delay this decision. The Emancipation Proclamation over time would reinforce the political liability of supporting the Confederacy. Despite sympathy for the Confederacy, France's own seizure of Mexico ultimately deterred them from war with the Union. Confederate offers late in the war to end slavery in return for diplomatic recognition were not seriously considered by London or Paris. After 1863, the Polish revolt against Russia further distracted the European powers, and ensured that they would remain neutral.[213]
Date: 2016-07-25; view: 225; Нарушение авторских прав; Помощь в написании работы --> СЮДА... |