
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Fig. 6
Effects of taxifolin on the synthesis and secretion of 35S-labeled apoB, apoA-I, and albumin during a 120- or 180-min chase. HepG2 cells were grown, treated, and pulse-chased as described in Fig 5. The intracellular fraction was collected at the beginning of the chase (peak incorporation), whereas the extracellular fraction was collected at the end of the chase period (peak secretion). The samples were subjected to immunoprecipitation of apoB, apoA-I, and albumin. Bar graph summarizes the data on apoB, apoA-I, and albumin synthesis and secretion relative to control (set as 100%). Data represent means ± SD of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. * P < 0.05 versus control.
In parallel, the amount of apoA-I secreted in the presence and absence of taxifolin was also analyzed (Fig. 5B). Interestingly, a 35% increase in apoA-I secretion in taxifolin-treated cells was observed when compared with untreated control. A similar increase was noted for its synthesis rate (38%; reproduced in two other independent experiment; results pooled in Fig. 6). The increase in apoA-I secretion suggests that the inhibitory effect of taxifolin on apoB secretion is specific and that taxifolin may have benefits related to high density lipoprotein (HDL) metabolism.
As another control, the fate of nascent albumin synthesis and secretion were also examined during the chase. Results from three independent experiments performed in duplicate are summarized in Fig. 6. Measurement of albumin was done by immunoprecipitation, SDS-PAGE, and fluorography. A consistent increase in the synthesis of albumin (42 ± 4%, P < 0.05, n = 3) was observed at the beginning of the chase. The increase in synthesis corresponded to an increase in albumin secretion (16 ± 1%, P < 0.05, n = 3) at the end of the chase. This further suggests that the inhibitory effect of taxifolin on apoB secretion is indeed specific. The increase in albumin and apoA-I syntheses is interesting and may reflect a global transcriptional effect. This is compatible with the mechanism of action of silybin, a flavolignan containing a taxifolin moiety, which can influence RNA polymerase activity (18).
Taxifolin has no effect on apoB and apoA-I mRNA steady-state levels
Our previous experiment indicated that the effect on apoB and apoA-I secretion appeared to be exerted at the synthesis level of these apolipoproteins. To address whether their transcription rate may be involved, a sensitive RNase protection/solution hybridization assay was used to measure apoB and apoA-I mRNA steady-state levels. Under our conditions (200 μM taxifolin, 24 h), hepatic apoB and apoA-I mRNA abundances remained essentially unchanged when compared with the untreated control cells (Table 1). This rules out transcriptional effects and indicates that other regulatory mechanism(s) are being exerted.
Taxifolin decreases the secretion of apoB into LDL-like particles
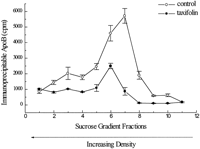
To examine the distribution of secreted apoB-containing lipoprotein (apoB-Lp) with taxifolin, the density of secreted apoB-Lp particles in HepG2 cells was investigated by sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation. ApoB-Lp secreted by cells was observed to have a similar density to that of human plasma LDL, as has been observed in several studies [reviewed in ref. (19)]. As depicted in Fig. 7, taxifolin markedly reduced the amount of secreted apoB-Lp with a slight shift in the density profile of secreted particles (fractions 2–5 represent dense HDL-like apoB-Lp, whereas fraction 6–12 represent LDL-like apoB-Lp). This suggests that taxifolin and perturbed lipid synthesis can partially block the secretion of apoB-Lp particles. Whether taxifolin affects the assembly process of apoB-Lp particles will require further investigation.
View this table:
· In this window
· In a new window
TABLE 1.
ApoB and apoA-I mRNA abundances in control and taxifolin-treated cells a
Taxifolin stimulates apoB degradation via a DTT-sensitive, ALLN-insensitive proteolytic pathway
Intracellular proteasomal degradation of apoB has been well described as the major regulatory mechanism of action in apoB-Lp secretion (19, 20). To determine whether ALLN-sensitive proteasome is involved in the taxifolin-induced changes in apoB secretion, pulse-chase experiments were performed. Taxifolin-treated and untreated control cells were pretreated for 10 min with and without ALLN (20 μg/ml) and taxifolin. After a 10-min pulse, the cells were chased for 5 min and harvested for apoB immunoprecipitation. As shown in Fig. 8, addition of ALLN to the untreated control cells (lanes 9 and 10) failed to accumulate apoB intracellularly, indicating a probable rapid cotranslational degradation of apoB. In the presence of taxifolin (Fig. 8, lanes 11 and 12), apoB cellular content was further reduced and was not blocked by ALLN. This suggests that other protease(s) may be responsible for apoB degradation.
View larger version:
· In this page
· In a new window
· Download as PowerPoint Slide
Date: 2015-09-18; view: 204; Нарушение авторских прав; Помощь в написании работы --> СЮДА... |