
Полезное:
Как сделать разговор полезным и приятным
Как сделать объемную звезду своими руками
Как сделать то, что делать не хочется?
Как сделать погремушку
Как сделать так чтобы женщины сами знакомились с вами
Как сделать идею коммерческой
Как сделать хорошую растяжку ног?
Как сделать наш разум здоровым?
Как сделать, чтобы люди обманывали меньше
Вопрос 4. Как сделать так, чтобы вас уважали и ценили?
Как сделать лучше себе и другим людям
Как сделать свидание интересным?

Категории:
АрхитектураАстрономияБиологияГеографияГеологияИнформатикаИскусствоИсторияКулинарияКультураМаркетингМатематикаМедицинаМенеджментОхрана трудаПравоПроизводствоПсихологияРелигияСоциологияСпортТехникаФизикаФилософияХимияЭкологияЭкономикаЭлектроника

Edge boundary condition and inter-valley scattering
Now we discuss the relation between the inter-valley scattering and edge boundary condition. According to [5], the impurity potential can be included in the massless Dirac equation by adding the following potential term U ˆ imp described as
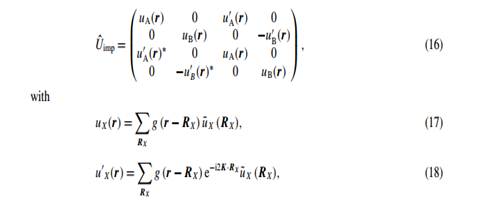
where u ˜ X (R X) is the local potential due to impurities for X = A or B. Here g (R) with the normalization condition of P R g (R) = 1 is a real function, which has an appreciable amplitude in the region where | R | is smaller than a few times of the lattice constant, and decays rapidly with increasing | R |. For convenience we distinguish the impurity into two types by the range of the impurity potential: one is LRI if the range of impurity potential is much larger than the lattice constant and the other is SRI if the range of impurity is smaller than the lattice constant.
If only the LRIs are present, we can approximate u A(r) = u B(r) ≡ u (r) and u 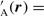 u 0B(r) ≡ u 0(r). In the case of carbon nanotubes and zigzag nanoribbons, u
u 0B(r) ≡ u 0(r). In the case of carbon nanotubes and zigzag nanoribbons, u 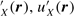 X vanishes after the summation over R X in equation (18) since the phase factor e−i2 K · R strongly oscillates in the x -direction. This means that the two valleys are independent and one can only focus on either the K + or K − valley. Thus LRIs do not induce inter-valley scattering for zigzag nanoribbons.
X vanishes after the summation over R X in equation (18) since the phase factor e−i2 K · R strongly oscillates in the x -direction. This means that the two valleys are independent and one can only focus on either the K + or K − valley. Thus LRIs do not induce inter-valley scattering for zigzag nanoribbons.
However, this cancelation is not complete in an armchair nanoribbon because the averaging over the x -direction is restricted to the finite width of W. This means that we cannot neglect the contribution from scatterers particularly in the vicinity of the edges to u 0 X (r). This means that inter-valley scattering does not vanish even in the case of LRI in the armchair nanoribbons.
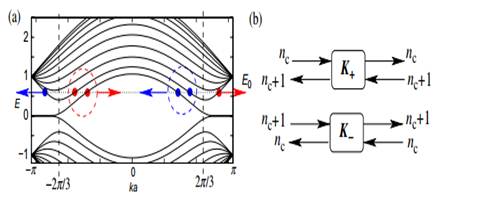
Figure 6. (a) Energy dispersion of zigzag ribbon with N = 10. The valleys in the energy dispersion near k = 2π/3 a (k = −2π/3 a) originate from the Dirac K +(K −)-point of graphene. The red-filled (blue-unfilled) circles denote the right (left)-moving open channel at the energy E 0 (dashed horizontal line). In the left (right) valley, the degeneracy between right and left moving channels is missing due to one excess right (left)-going mode. The TRS under the intravalley scattering is also broken. (b) Schematic figure of scattering geometry at K + and K − points in zigzag nanoribbons, where a single excess right-going mode exists for the K − point, but a single excess left-going mode exists for the K − point. Here nc = 0,1,2,....
Date: 2015-05-09; view: 516; Нарушение авторских прав; Помощь в написании работы --> СЮДА... |